Significance of Gas Pressure Vessels
Significance of Gas Pressure Vessels

Importance of Regular Maintenance
Pressure reducing regulators can be classified into two main categories single-stage and two-stage regulators.
In conclusion, relief valves are indispensable components in the safe operation of numerous industrial processes. They provide critical protection against overpressure, contributing to the safety and longevity of equipment while also safeguarding the well-being of personnel. Understanding the types, applications, and importance of relief valves can help industries maintain effective pressure management and ensure compliance with safety standards. As technology continues to advance, the design and functionality of relief valves will likely evolve, further enhancing their capability to protect equipment and personnel in increasingly complex systems.
4. Safety Features Safety is paramount when designing pressure vessels. Engineers incorporate features such as pressure relief valves, rupture disks, and proper anchoring to prevent catastrophic failures. Regular inspections and maintenance are also essential to ensure the vessel remains safe over its operational lifetime.
4. Relief Valves These are safety devices that release excess pressure in a system. When the pressure exceeds a predetermined limit, the relief valve opens to allow air to escape, thus protecting other components from damage.

Gas heat exchangers are employed across various industries including automotive, aerospace, power generation, and manufacturing. In power plants, they are used to recover waste heat from exhaust gases, which can then be converted into useful energy, enhancing the overall efficiency of the plant.
2. Safety The built-in safety features help mitigate the risks associated with pressure fluctuations, protecting both equipment and personnel.
Pressure regulating valves (PRVs) are crucial components in a wide range of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. These valves maintain a consistent output pressure by adjusting the flow of fluid within a system, regardless of variations in inlet pressure or downstream demand. As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and safety, the role of pressure regulating valves has become more significant than ever.
Advantages of Using Pressure Reducing Regulators
Understanding Gas Safety Relief Valves Importance and Functionality
In the world of design and technology, the term separator plays a crucial role across various fields, from graphic design to software architecture. At its core, a separator serves as a marker, divider, or distinction between elements, allowing for better organization and clarity. This article explores the multifaceted nature of separators, their applications, and their significance in our daily lives.
The growing demand for LNG can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, as developing nations industrialize and urbanize, their energy needs have soared. Countries like China and India are investing heavily in LNG infrastructure to meet their burgeoning energy demands while also making commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the shale gas revolution, particularly in the United States, has led to an abundance of natural gas, driving down prices and making LNG more competitive on the global market.
Automated cleaning systems have also been developed, minimizing manual intervention and reducing downtime. By incorporating automation and advanced materials, today's filter separators are more effective, reliable, and easier to maintain compared to their predecessors.
4. Scalability As organizations grow and their data needs increase, coalescing filters provide a scalable solution that enables them to handle growing data volumes without compromising on performance.
One of the most significant advantages of LNG is its lower environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels. When burned, LNG emits about 50% fewer carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to coal and around 30% less than oil. Moreover, it produces virtually no sulfur dioxide (SO2) or particulate matter, which are significant contributors to air pollution and health problems. As countries grapple with climate change and strive for greener energy solutions, LNG presents itself as a cleaner bridge fuel that can support a transition towards more sustainable energy production.

Furthermore, smart organizers often come equipped with features that promote collaboration. In an era where remote work and virtual teams are becoming increasingly common, the ability to share schedules and tasks with colleagues is essential. Smart organizers facilitate seamless communication by enabling users to synchronize their calendars, share documents, and assign tasks to team members. This fosters a sense of unity and improves overall team efficiency, as everyone stays informed and engaged in the same project or goal.
Natural gas regulators play a crucial role in the safe and efficient distribution of natural gas, which is widely used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. As a vital component of gas infrastructure, regulators ensure that gas is delivered at the appropriate pressure to consumers while maintaining safety standards and operational efficiency.
A pressure reducing valve is a mechanical device that automatically reduces and maintains the pressure of a fluid to a desired level. Typically installed downstream of a pressure source, PRVs let fluid flow to downstream processes while keeping the pressure consistent and within safe limits. By limiting the pressure, these valves protect delicate equipment from potential damage, leaks, or failures caused by excessive pressures.
4. Flow Control Valves These valves maintain a consistent flow rate in pneumatic systems. They can be adjusted to regulate speed in actuators and other devices.
Moreover, natural gas serves as an essential complement to renewable energy sources. Wind and solar power, while increasingly cost-effective and essential for a clean energy future, often face intermittency issues—meaning they do not consistently produce electricity when demand is high. Natural gas plants can quickly ramp up or down their output to balance the grid, providing a reliable backup that helps stabilize energy supplies. This flexibility makes natural gas an ideal partner for renewable energy, facilitating the gradual integration of more green energy sources into the existing power infrastructure.

There are several types of PRVs, each designed for specific applications

One key factor to consider in the design of gas-to-gas heat exchangers is the heat transfer coefficient. This coefficient measures the rate at which heat is transferred between the two gas streams and is influenced by factors such as surface area, flow velocity, and fluid properties. Increasing the heat transfer coefficient can improve the efficiency of the heat exchanger and reduce energy consumption.
Pressure Regulating Skids Ensuring Safety and Efficiency in Fluid Transport
- Efficiency By maintaining appropriate flow rates and pressures, regulating valves enhance the efficiency of systems, decreasing energy consumption and operational costs.
In addition to healthcare, NG is reshaping the transportation industry. As autonomous vehicles continue to gain traction, the reliance on sophisticated networks becomes paramount. Next Generation Networks provide the backbone for real-time communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and users, ensuring safety and efficiency. Imagine a world where traffic congestion is alleviated by smart traffic systems that adapt based on real-time data from connected cars. This vision is not a distant dream but a tangible reality made possible by NG technologies.
Despite its potential, gasification technologies and equipment face challenges, including high capital costs, the need for advanced engineering, and the requirement of skilled personnel for operation. However, ongoing research and development are focused on overcoming these hurdles, making gasification a more accessible and economically viable alternative for energy production.
Understanding these types is crucial for engineers when selecting the right valve for their specific application, ensuring optimal performance and safety.

Despite their importance, distribution stations face several challenges. The increasing complexity of global supply chains, fluctuating consumer demands, and geopolitical uncertainties can disrupt the flow of goods. Additionally, the ongoing digital transformation in logistics requires continuous investment in technology and workforce training. Operators must be agile and adaptive to overcome these challenges while maintaining service quality and efficiency.
Furthermore, CNG infrastructure is expanding rapidly, with an increasing number of refueling stations being established in urban and rural areas. These developments are crucial for encouraging the adoption of CNG as a mainstream fuel choice. While the initial investment for converting vehicles may be high, the growing availability of refueling stations is making it easier for consumers to make the switch. Governments are also playing a role in this transition; incentives and rebates are often available to promote the adoption of CNG vehicles and the construction of refueling stations.
Conclusion

 Additionally, the hose is designed to prevent refrigerant leaks, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively Additionally, the hose is designed to prevent refrigerant leaks, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively
Additionally, the hose is designed to prevent refrigerant leaks, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively Additionally, the hose is designed to prevent refrigerant leaks, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively sae j2064 air conditioning hose.
sae j2064 air conditioning hose.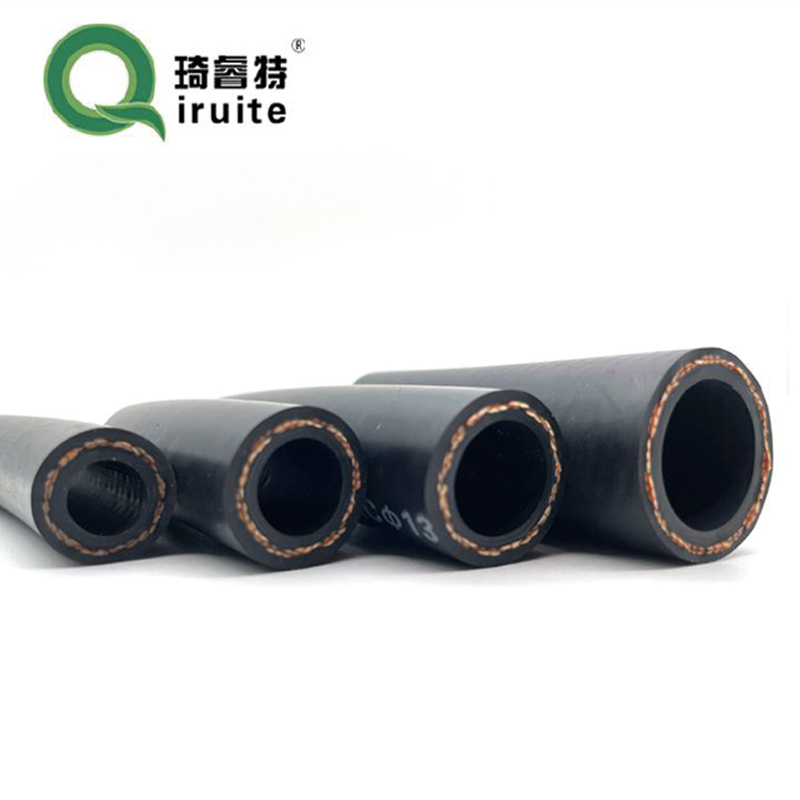
 Look for cracks, tears, or discoloration, which can indicate that the o-ring needs to be replaced Look for cracks, tears, or discoloration, which can indicate that the o-ring needs to be replaced
Look for cracks, tears, or discoloration, which can indicate that the o-ring needs to be replaced Look for cracks, tears, or discoloration, which can indicate that the o-ring needs to be replaced ford power steering hose o-rings. If you notice any leaks or unusual noises coming from the power steering system, it is also a good idea to have the hose and o-rings inspected by a qualified mechanic.
ford power steering hose o-rings. If you notice any leaks or unusual noises coming from the power steering system, it is also a good idea to have the hose and o-rings inspected by a qualified mechanic. spiral wire cable protector. They are typically made from materials like plastic or metal, which offer varying degrees of protection based on the environment in which they are used. For example, in outdoor settings or areas with heavy machinery, metal protectors with high impact resistance might be preferred. In contrast, lighter-duty applications might only require plastic protectors.
spiral wire cable protector. They are typically made from materials like plastic or metal, which offer varying degrees of protection based on the environment in which they are used. For example, in outdoor settings or areas with heavy machinery, metal protectors with high impact resistance might be preferred. In contrast, lighter-duty applications might only require plastic protectors. This process often requires the use of specialized tools such as wrenches and sealants to prevent leaks This process often requires the use of specialized tools such as wrenches and sealants to prevent leaks
This process often requires the use of specialized tools such as wrenches and sealants to prevent leaks This process often requires the use of specialized tools such as wrenches and sealants to prevent leaks power steering hose adapter. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and inspect the connections for any signs of wear or damage before reassembling the system.
power steering hose adapter. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and inspect the connections for any signs of wear or damage before reassembling the system. This hose often runs along the passenger side firewall and can be secured with tie wraps or clamps to prevent vibrations and wear This hose often runs along the passenger side firewall and can be secured with tie wraps or clamps to prevent vibrations and wear
This hose often runs along the passenger side firewall and can be secured with tie wraps or clamps to prevent vibrations and wear This hose often runs along the passenger side firewall and can be secured with tie wraps or clamps to prevent vibrations and wear 69 mustang power steering hose routing.
69 mustang power steering hose routing.
